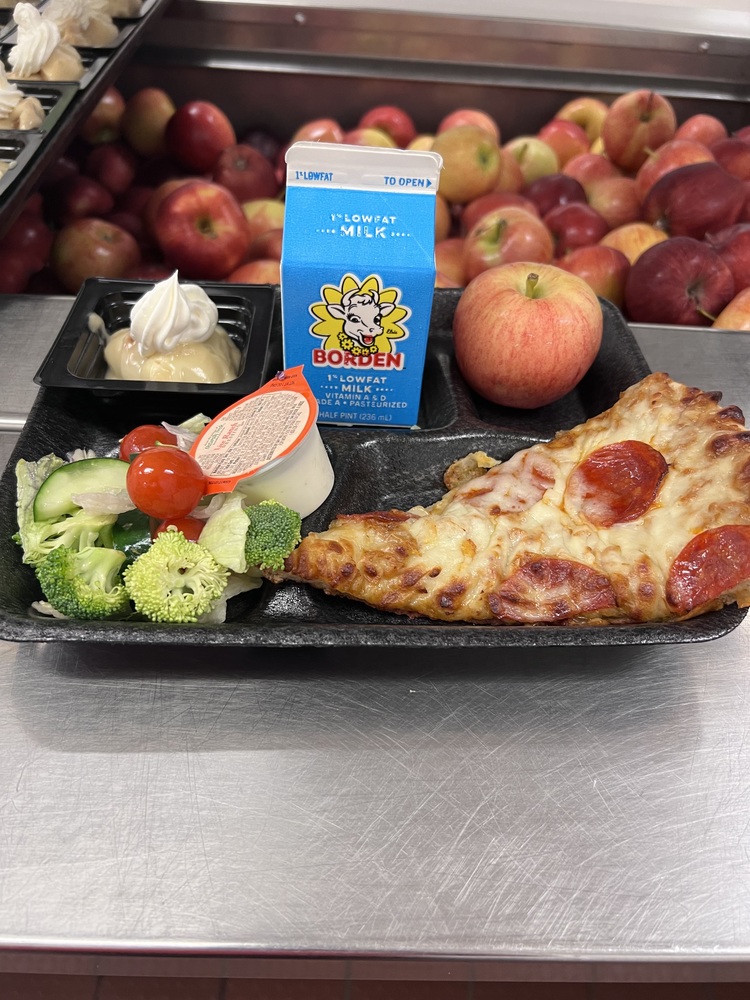
So—Michigan just adopted a policy of offering free breakfast and lunch to all K-12 public school kids. Charter school kids, too– and intermediate school districts (which often educate students with significant disabilities). More than half of Michigan students were already eligible for free-reduced lunch, which says a lot about why free at-school meals are critical to supporting students and their families. Why not streamline the system?
Schools have to sign up for the federal funding that undergirds the program, and still need income data from parents to determine how much they get from the feds. Nine states now have universal breakfast-lunch programs, and another 24 are debating the idea, which—in Michigan anyway—is estimated will save parents who participate about $850 year. That’s a lot of square pizza, applesauce and cartons of milk. Not to mention reducing stress, on mornings when everyone’s running late for the bus and work.
Cue the right-wing outrage.
Headline in The New Republic: Republicans Declare Banning Universal Free School Meals a 2024 Priority. Because? “Community Eligibility Provision, or CEP, allows certain schools to provide free school lunches regardless of the individual eligibility of each student.”
It’s hard to figure out precisely what they’re so honked off about: Poor kids getting something—say, essential nutrition– for nothing? Kids whose parents can well afford lunch mingling with their lower-income classmates over free morning granola bars and fruit? No way to clearly identify a free lunch kid in the 6th grade social hierarchy? The kiosks at the HS, where kids can grab something to give them a little fuel for their morning academics?
How will this all work out? It will take a couple of years, but school lunch services think they can figure out how to adapt. It will be a relief not to have three lunch lines. The kids who ran up lunch debt and were given a peanut butter sandwich will go incognito, and they can stop sending threatening emails to errant parents. All good.
Long-term, there is evidence that free, in-school breakfast and lunch improve learning and focus.Feeding them reasonably healthy snacks makes it more likely they’ll have fewer health problems. In fact, a wide array of research studies have tracked better attendance, fewer discipline events, and even benefits for families, giving them more money to purchase needed food and household goods.
Isn’t that what we’re all aiming for, as public school educators and government service providers?
The child poverty rate plummeted in 2021, thanks largely to a major, but temporary, boost to the child tax credit in the $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan Act. It beefed up payments to $3,600 for each child up to age 6 and $3,000 for each one ages 6 through 17, for lower- and middle-income families for 2021. That boost lifted 2.1 million children above the poverty line in 2021, according to the Census Bureau.
Now that the money is no longer coming in to struggling families, free breakfast and lunch, M-F, for the kids, would be a nice cushion, indeed. And schools, once again, are stepping up, to be the delivery system for an essential public good: feeding kids.
It’s what a rich nation—or state, at least— should be doing. Or so I think.
And yeah, I know about catsup is a vegetable and the fact that some school lunches are pretty unbalanced. I also know that some kids will never eat a school lunch, both kids whose mothers pack them delicious lunches, and kids who skip lunch because the cafeteria is a social nightmare.
None of that matters.
Do what we can to help feed kids. It’s the right thing to do.