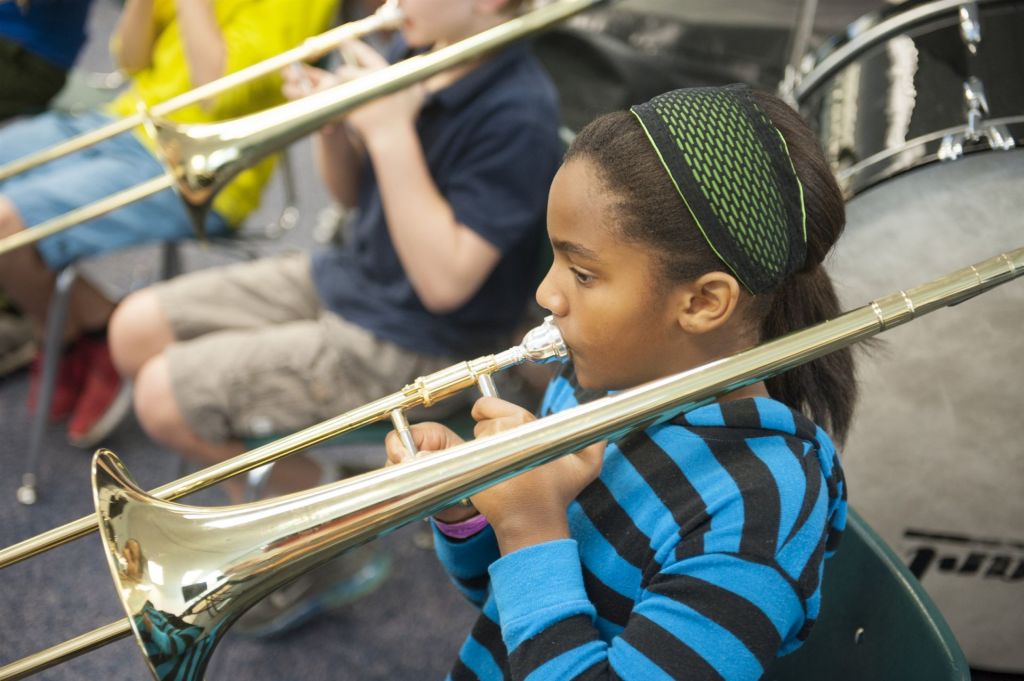I am fascinated by the increasing politicization—no other word for it—of reading instruction. How to best teach reading has always been contentious in the United States, from the 1950s look-say method featuring Dick and Jane, accused of letting Ivan slip ahead of us in the space race, right up until last week, when Moms for Liberty jumped into the Faux Science of Reading (FSoR) fray.
It’s unclear why Moms for Liberty has aligned itself with the phonics-forward FSoR movement. I get that white parents, accustomed to being first in line for educational goodies, feel threatened when they’re told that other children may be having their needs met first. I know racism is a thread that has run through the entire history of public education in America. I also know that many ordinary citizens feel bewildered and angered by rapidly changing social beliefs and customs around acceptance of the LGBTQ+ community.
A friend of my says you can measure social progress by observing who can be beat up on Saturday night without consequences—Wives and girlfriends? Ethnic minorities? Gentle souls like Matthew Shepherd and Elijah McLain? I hate living in a country where threats align with archaic ideas about who’s in charge of our customs and institutions, including public schools. I hate it, but I understand why it happens.
What I do NOT understand is why a far-right, power-grabbing, deep-pocket-funded group of purported “concerned moms” are choosing to endorse One Right Way to learn the skill of reading.
Surely some of their children learned to read using cuing systems or word walls or balanced literacy. Surely some of their children picked up reading quickly and easily reading stories on grandma’s lap. Surely some of their children had caring and creative teachers who employed multiple strategies to nurture genuine literacy.
Which makes me think that a lot of the enmity around learning to read stems from free-floating hostility toward public education and schoolteachers in general, greatly exacerbated by recent events: a pandemic, a child-care crisis, growing and dangerous inequities, and terrible political leadership that plays to the worst in human nature.
John Spencer, an especially smart edu-buddy, recently posted a long, thoughtful tweet about what he called the phonics-centric Science of Reading approach for older students— middle school kids, for example, who theoretically should already be ‘reading to learn.’ He muses about encouraging reading for pleasure, and to build endurance, more than discrete skills. He notes that a one-size approach to decoding words is inappropriate for young teenagers. His last two points were key: most of the people advocating for the so-called “Science” of reading hadn’t read or didn’t understand the research, and that there are multiple assistive tools (audio readers, for ex) that can help kids learn to love reading.
What followed was a long discussion thread, mostly probing and expanding John’s well-considered ideas. But a couple of hours later, he posted this:
I wrote a long tweet about my concerns in using Science of Reading approaches with middle school students. Not a critique. Just a set of concerns. Getting some angry responses in my DMs. Each one fails to address my 5 points. All of them resort to personal attacks. Most of them somehow frame this as a partisan political issue. Wild.
And… there it is. Again. Politicizing the very heart of teachers’—TEACHERS’– professional work. Why is that happening?
I have written several published pieces about learning to read. Like John, I have received angry responses, mostly centered on the fact that I am not a reading teacher, and therefore, have no expertise.
The fact is: I have taught approximately 4000 children, over 32 years, to read music, in order to play a band instrument. Most of them were 5th and 6th grade beginners, aged 10-12. They may have had earlier experiences—piano lessons, say, or the church choir—in reading music (similar to first graders who come to school with dozens of sight-words already mastered), but most were not musically literate at all when they came to me.
They learned in large, mixed-instrument groups, using method books in which everyone necessarily goes at a glacial pace. In addition to understanding a completely new set of symbols designating pitch, duration, silence, articulations and tempo, they have to struggle with making pleasant and consistent sounds on a complex device.
It’s incredibly difficult. The interesting thing is that some kids who excel at traditional school tasks—including reading and math, the skills we value most—find learning to play an instrument very frustrating, especially when other students, academic lesser lights, quickly pick up tunes via watching, listening and repetition.
Good instrumental music teachers quickly learn that slogging through the method book, day in and day out, one new note at a time, will kill off the rabid enthusiasm for playing in the band that your average fifth grader displays on the night he gets his new trumpet.
These teachers turn to ideas similar to what John Spencer references: Playing by ear for pleasure or long tone contests to build endurance. Multiple modalities of playing (watching, repeating, chord-building) besides straight-up note-reading. Playing with CDs. Bringing in older students who demonstrate what fun it is to play music in groups. Encouraging students to make up songs, or pick out a popular tune.
The key is the first performance where everyone (including the kids who don’t yet know correct note names or how to interpret a key signature) plays that six-note version of Jingle Bells, and families go home happy. A huge part of being a beginning band teacher is herding all the kids forward, even though they’re learning different things at wildly different rates, and making the whole process joyful.
There are, of course, instrumental music teachers who insist that there is only one way to teach kids to read music and play an instrument. How can you play music if you don’t know that the third space treble clef is a C, and a dotted note gets one and a half times the value of the original note? Start at the beginning, and don’t move ahead until everyone gets it. The method book as ‘settled science.’
The truth is that breaking down music-reading skills into discrete bits—like phonics, in reading– is only one of a palate of options; the motivated student can always cycle back to pick up new knowledge or techniques once curiosity and love are established.
Good teachers at all levels and subjects set kids free, tapping their natural abilities and making things joyful. The Faux Science of Reading wants every child to learn in the same way, just like the Moms for Liberty want children to read the same books and believe the same things about who has power in this country.