I got my master’s degree in gifted education—actually, a master’s in curriculum and instruction with an emphasis on identifying and serving gifted students, but whatever. At the time—the 1980s—I was focused on the ‘talented’ part, as a music teacher.
What could I do, I wondered, to better understand and challenge the exceptionally proficient students who showed up in my band room? There had only been a handful, at that time, students who leapt over my pedestrian instruction, right into credible Mozart concertos in the 6th grade, relying on recordings and (this sounds so quaint) library books about the great composers and their style characteristics.
I had many thoughtful conversations with people in my master’s classes, in my building, and fellow band directors (whose advice was generally directed toward private lessons and summer camps–the ‘better teacher/better cohort’ theory). But overall, takeaways on who was gifted and what to do about it were murky.
One person’s budding genius was another teacher’s ho-hum. A lot of it had to do with perceived student effort, and very little was about digging gifts and talents or even preferences and goals out of kids who were content to skate by.
Also, lots of kids who had exceptional natural talent in playing instruments were not so gifted in other areas, and therefore not interesting to the guy teaching Algebra II to 7th graders. Just because you can flawlessly pick up salsa rhythms with all four of your limbs or produce a crystalline high C on the trumpet doesn’t mean you’re… gifted. Or so it seemed.
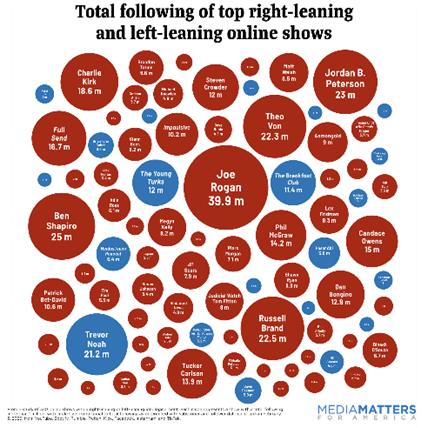
I’ve written many pieces—here, here, here, here and here, for example—about giftedness. Invariably, they draw nasty comments. It’s very much a tender spot for parents of bright children who worry that their children are not being adequately challenged. Or are ignored by their teachers because so many other kids are struggling or misbehaving. I get it.
But I also know that talents and gifts are randomly distributed across school populations and have to be developed over time, with the cooperation of the identified GT student. I was struck by this quote from a spokesperson for Mayor Zohran Mamdani, reflecting on the mayoral decision not to test kindergarteners to determine who’s gifted:
This administration does not believe in G. & T. evaluation for kindergartners. But that’s not the same as eliminating advanced opportunities across all grades.
My thoughts, precisely.
I recognize that NY City is unique—such a diverse population, so many school options, such hot politicking and parent-pleasing—but I fully agree with the mayor (or his advisor, more likely): Testing five-year olds for giftedness is ridiculous and bound to siphon off disadvantaged kids before they’ve really had a chance to, you know, go to school and learn stuff.
It’s the ultimate, rigged-end game: the outcomes of inequality, right out of the chute. Dividing the herd, yet again. Why? How does that help us?
If I had faith in any test to identify extraordinary, socially useful intelligence, skills, or creativity, I might feel differently. But I don’t. What I do believe is that all children deserve a rich and challenging education, whether a test identifies them as potentially brainy or sub-par. You just never know what role they might play, eventually, in making the world better.
Since more than half of American teens now admit to using chatbots to do “research” that they may not be able to evaluate for veracity, to write and calculate for them, it’s going to get harder and harder to distinguish students who produce genuinely brilliant work from those who are merely good at disguising where that work product originated.
We still need brilliant original work—not to feed the AI maw, but to enlighten ourselves, cure diseases, prevent wars, create peace, to explore, entertain and inspire. We need the indisputably brilliant kid who plays salsa rhythms but forgets to turn in his social studies worksheets for some reason. Because he has gifts to share.
We need a new definition of ‘gifted’—and maybe one for ‘talented’ as well. We need to stop accepting the assertion that machines are helping students learn better than human interaction and judgment. And most of all—we need to stop cutting kids off at the pass, sorting and labeling them when they’re in kindergarten.
Photo:sanbeiji (Creative Commons)